The Control unit, ALU, and Registers are collectively known as a Central Processing Unit (CPU).
A Central Processing Unit (CPU), is also called a Central Processor or Main Processor.
Early CPUs were composed of many separate components. Since the 1970s, CPUs have typically been constructed on a single MOS integrated circuit chip called a Microprocessor.
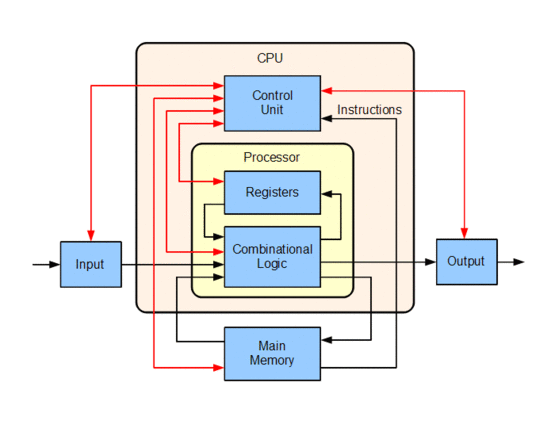
CPU executes instructions that collectively make up a "computer program".
A Computer program is a collection of instructions that can be executed by a computer to perform a specific task or multiple tasks. Most computer devices require programs to function properly.
Computer program is discussed in later chapters.
The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions in the program.
Most modern CPUs are microprocessors, where the CPU is contained on a single metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) chip.